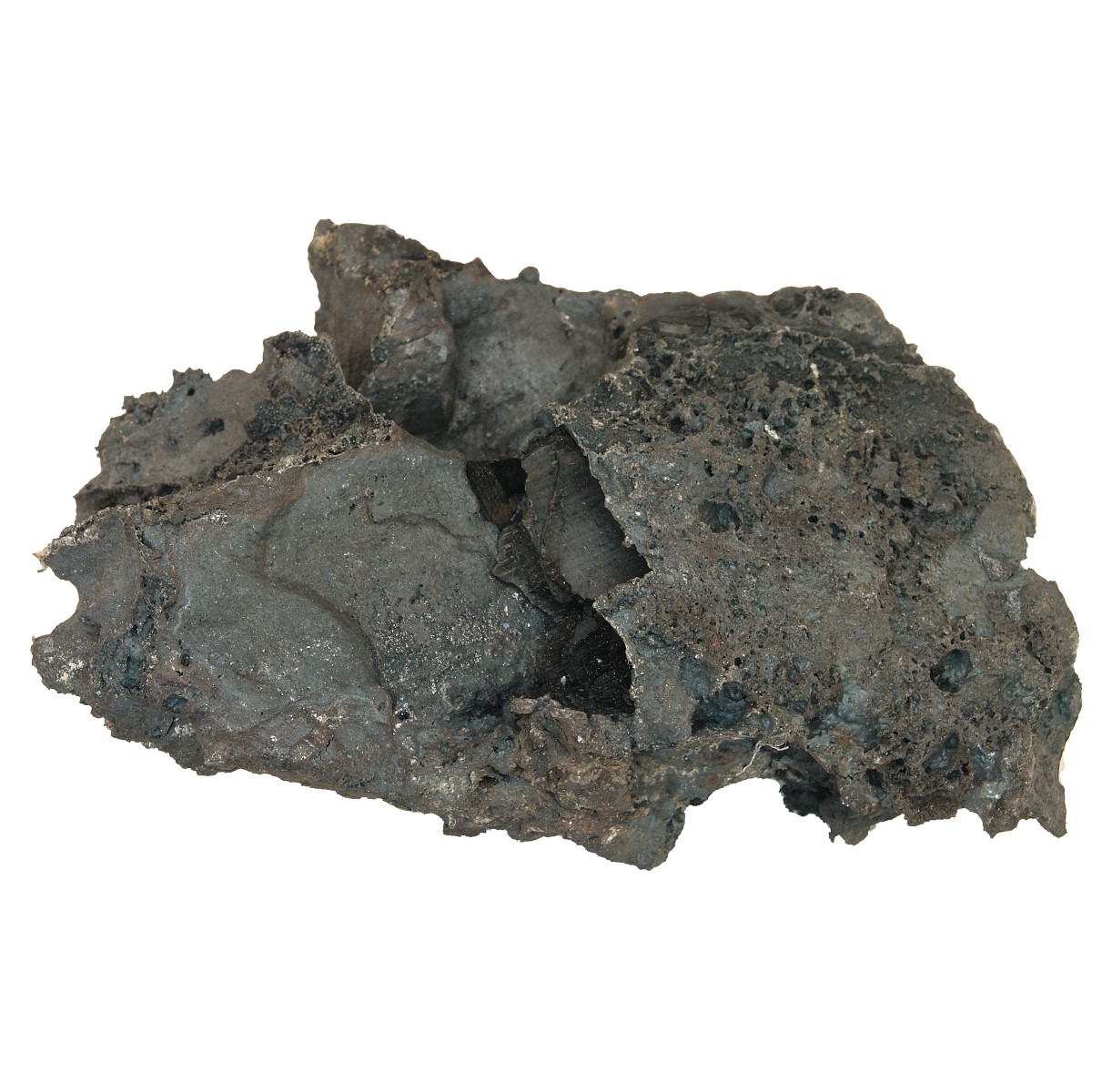
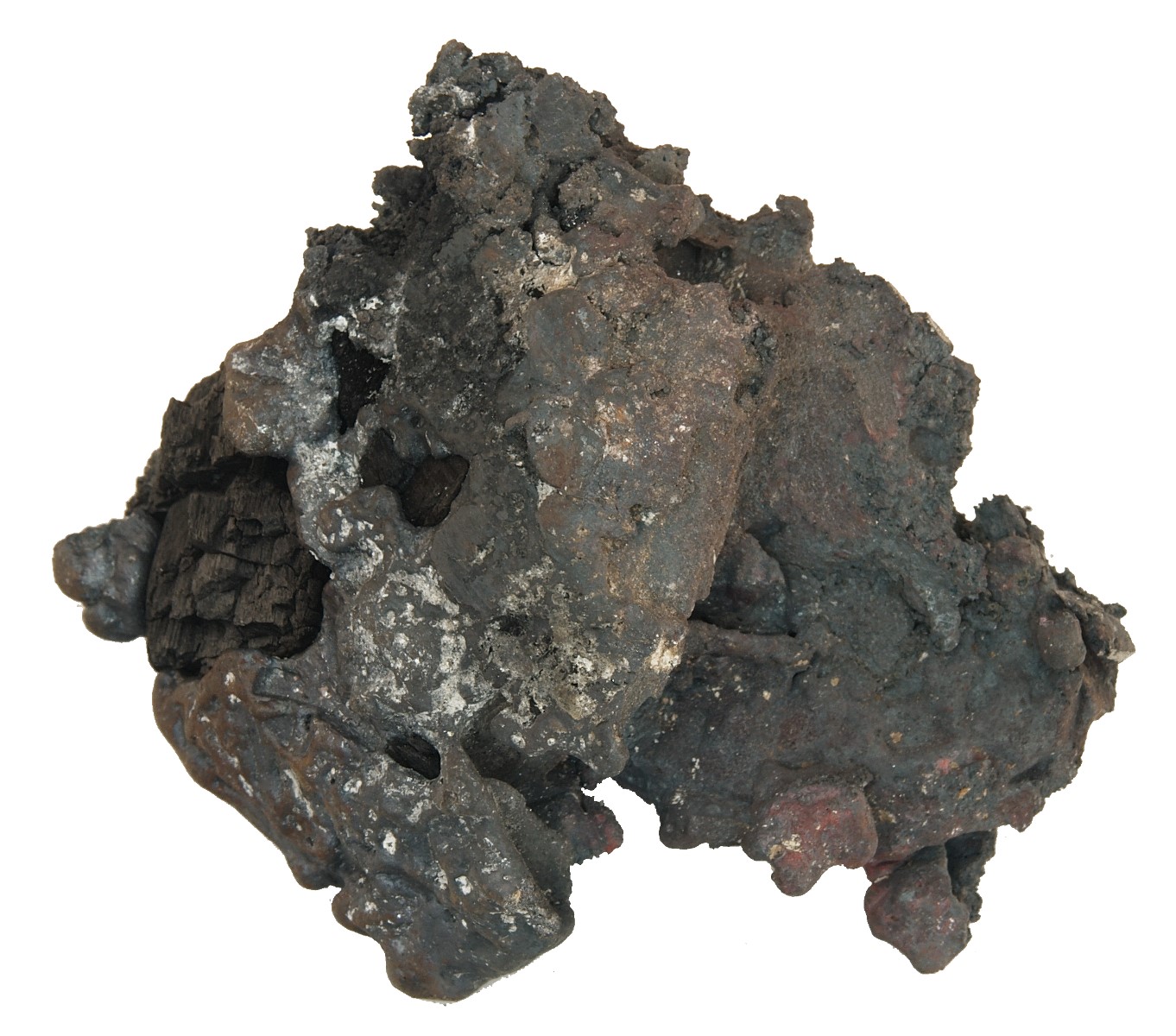
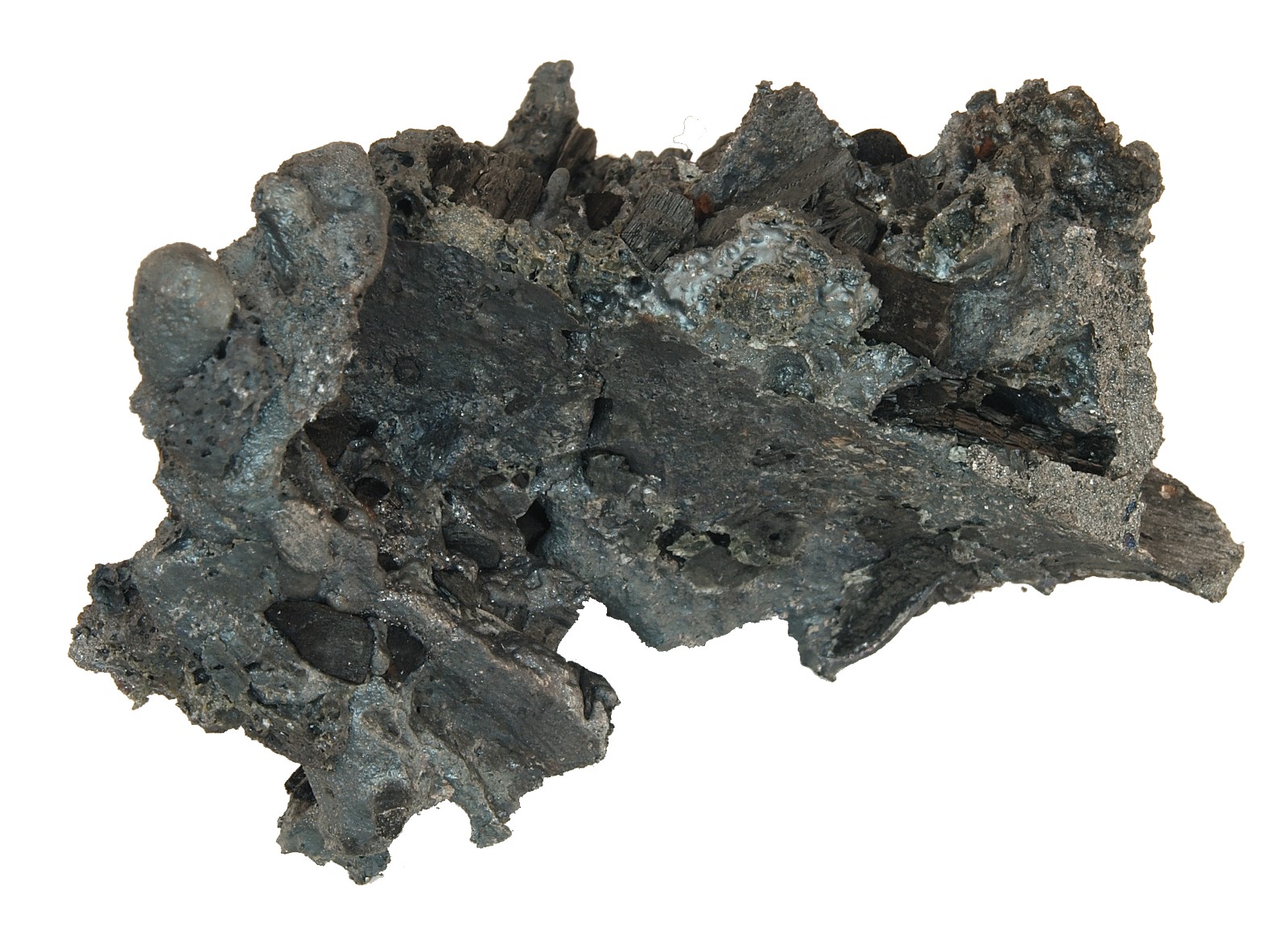
loop, unforged 1,1 kg
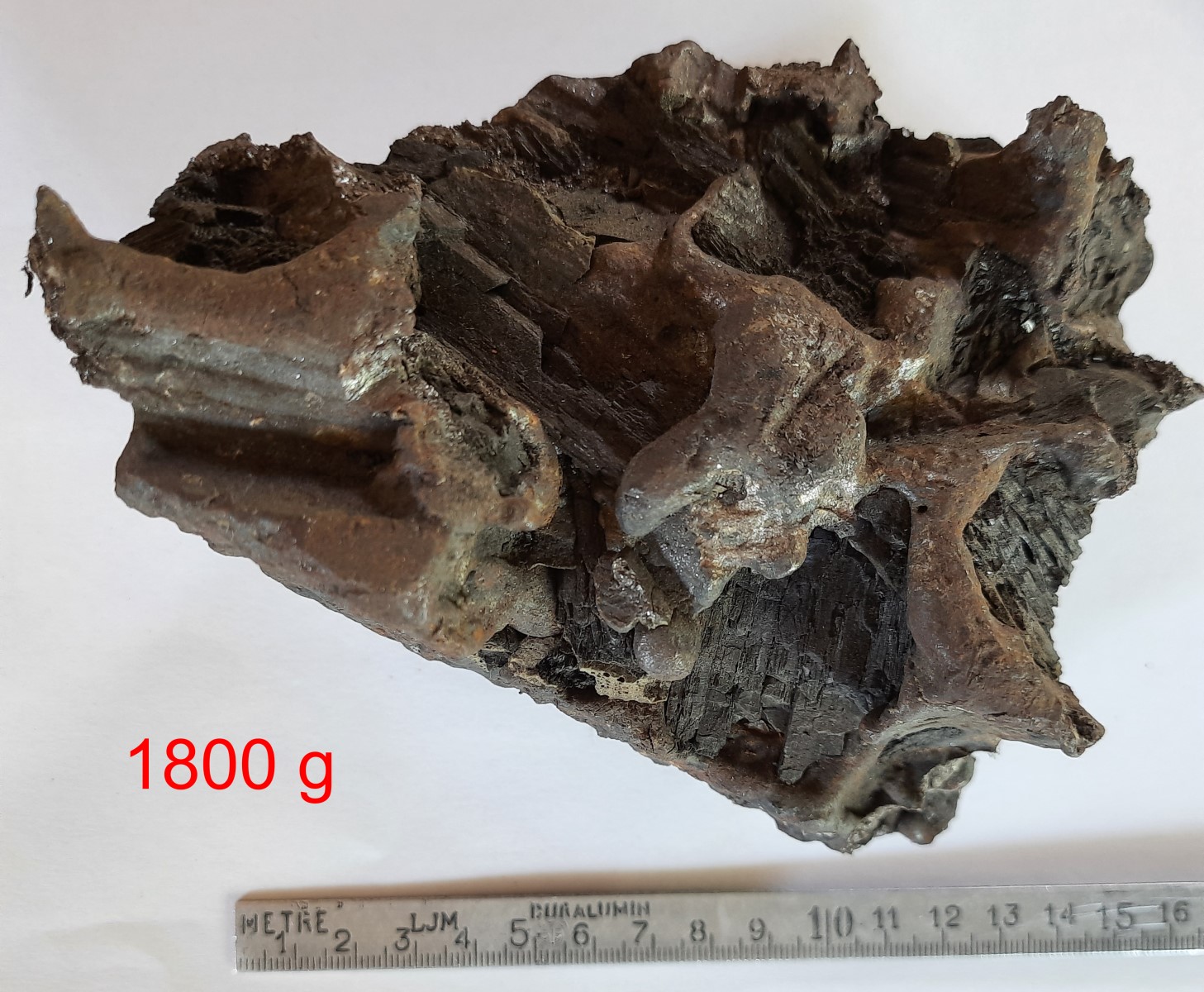
Ingot, raw, unforged, from the blast furnace
Carbon content up to approximately 1.6% in the raw ingot
Forged, typically approximately 0.6-0.8%. These values are purely approximate and can vary considerably.
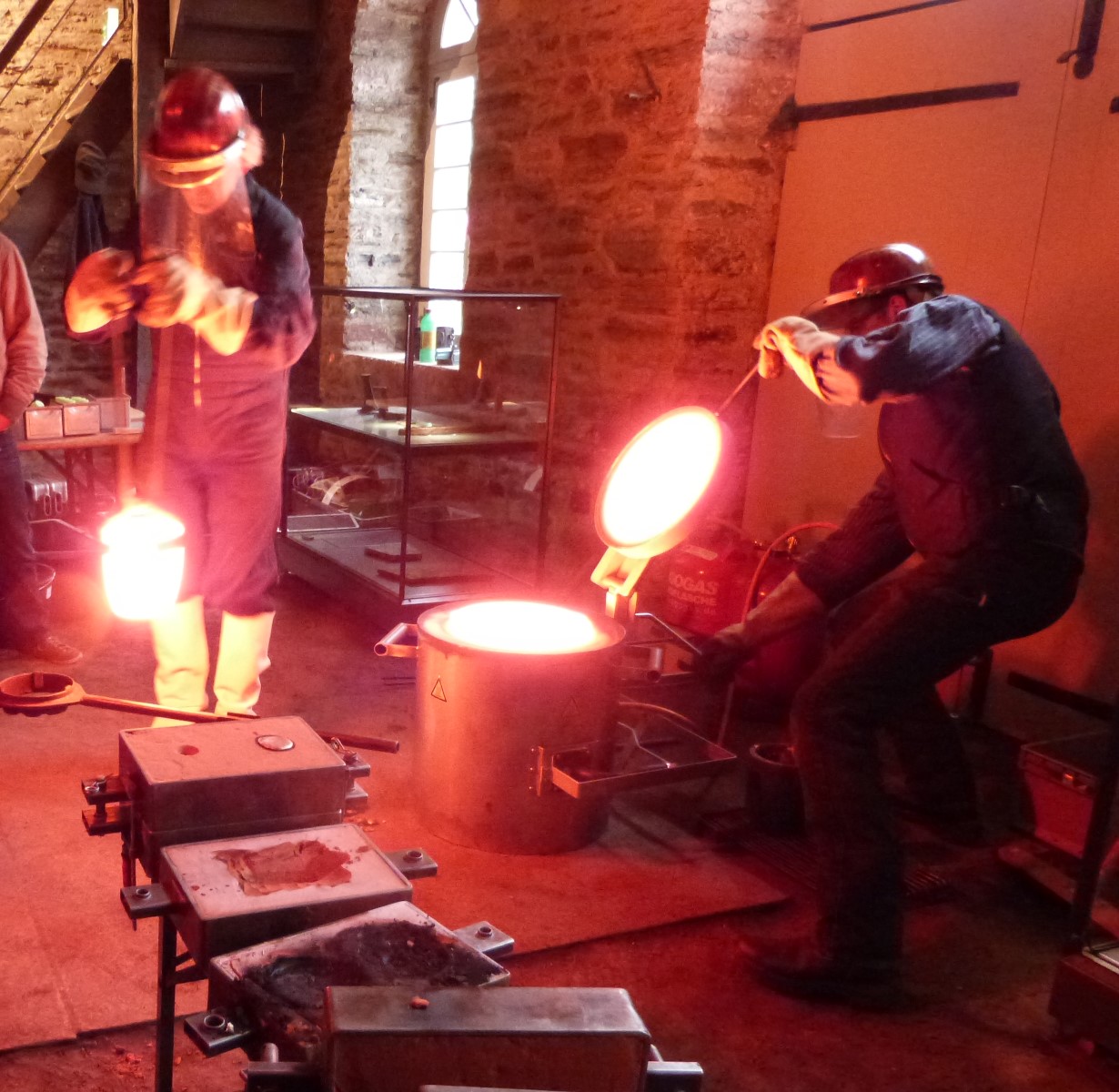
Until the development of blast furnaces in the late Middle Ages, iron was produced in blast furnaces or blast hearths. Temperatures in these furnaces are only around 1200–1300°C. Therefore, the iron does not melt in the blast furnace; instead, the rock residue contained in the iron ore liquefies at these temperatures and flows (hence the name!) into the lower part of the furnace.
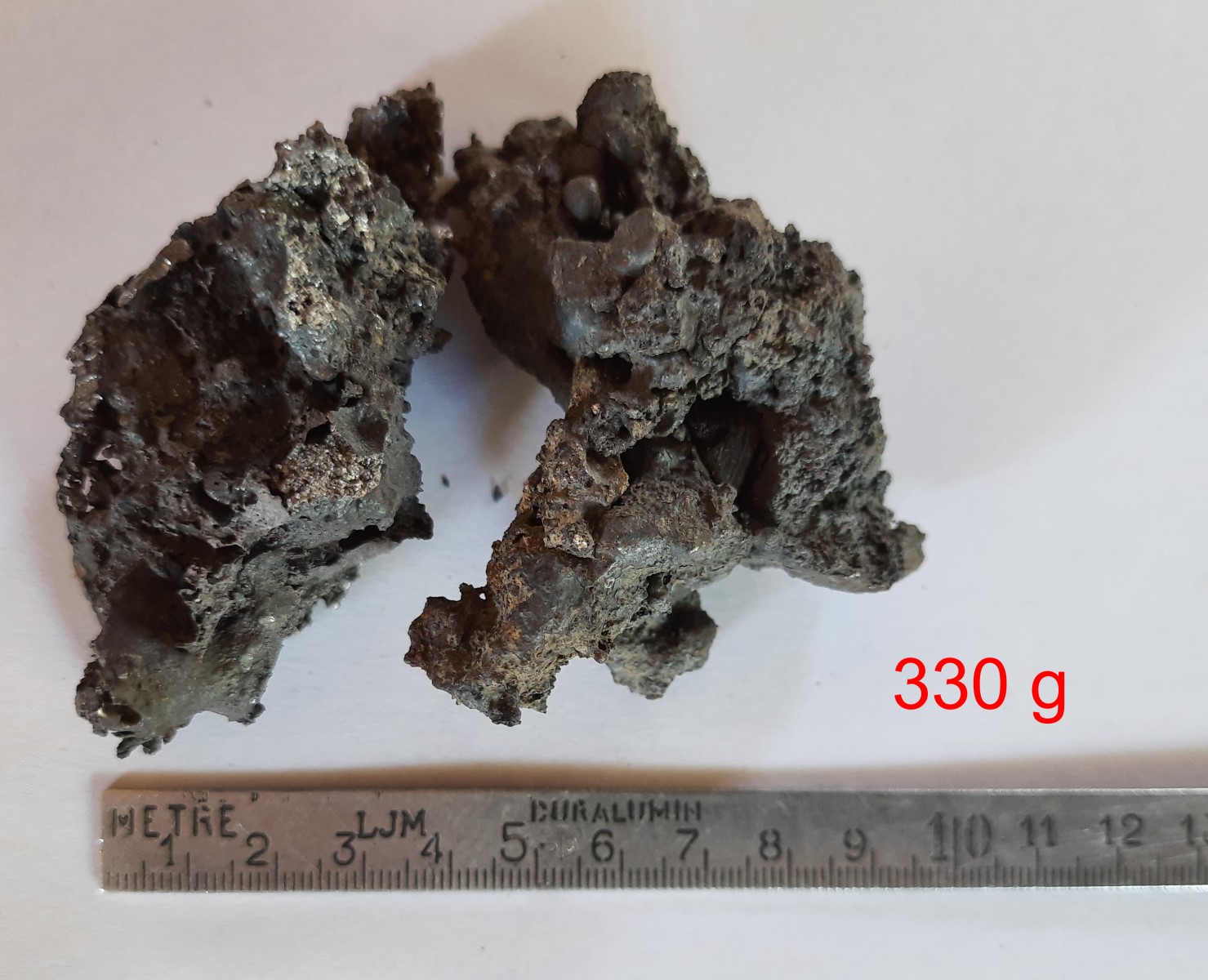
The remaining, slag-containing, spongy lump of iron is called a lump of ingot, and must be removed from slag and charcoal residue by folding and hammering to produce pure iron.
Information on product safety:
- Use only for users familiar with the product.
- Only for the intended purpose.
- Improper use can lead to damage and injury. Please also note the safety instructions included with the product.
Importer/manufacturer/distributor (unless another manufacturer is explicitly mentioned for the article):
ANGELE GmbH | Ringstrasse 25 | 88416 Ochsenhausen | Germany
info@angele-shop.com
Information on product safety:
- Use only for users familiar with the product.
- Only for the intended purpose.
- Improper use can lead to damage and injury. Please also note the safety instructions included with the product.
Importer/manufacturer/distributor (unless another manufacturer is explicitly mentioned for the article):
ANGELE GmbH | Ringstrasse 25 | 88416 Ochsenhausen | Germany
info@angele-shop.com